Klinische Bedeutung
Bei Patienten mit autoimmunen Enzephalopathien finden sich Autoantikörper gegen neuronale Oberflächenantigene. Die Antikörper sind gegen Glutamatrezeptoren (Typ NMDA oder Typ AMPA), GABAB-Rezeptoren, DPPX, spannungsabhängige Kaliumkanäle (VGKC) bzw. VGKC-assoziierte Proteine (LGI1, CASPR2) gerichtet. Da diesen Antigenen direkt oder indirekt eine Rolle in der synaptischen Signaltransduktion zukommt, gehen die assoziierten Autoimmunitäten meist mit Anfällen sowie neuropsychiatrischen Symptomen einher und resultieren unter anderem in speziellen Formen autoimmuner limbischer Enzephalitis, Neuromyotonie oder Morvan-Syndrom. Diese schweren, zum Teil potenziell letalen Syndrome können sowohl nicht paraneoplastischer als auch paraneoplastischer Ätiologie sein, wobei die Häufigkeit eines zugrundeliegenden Tumors entsprechend den Antikörpertypen zwischen 10 % und 70 % variiert. Den Antikörpern kommt vermutlich eine kausale Rolle in der Pathogenese zu. Da adäquate Therapiemaßnahmen (immunmodulatorische Interventionen, Tumorresektion) bei der Mehrheit der Patienten zu einer weitgehenden Rückbildung der Symptomatik führen können, ist eine frühzeitige Diagnosestellung maßgeblich für eine gute Prognose.
Diagnostik
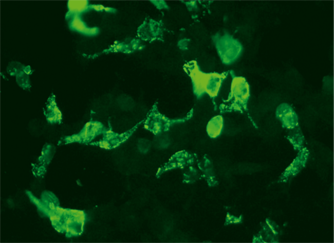 Die Diagnostik autoimmuner Enzephalitiden basiert im Allgemeinen auf der Kombination aus charakteristischem klinischem Bild, gegebenenfalls stützenden Befunden von Hirn-MRT, EEG und Liquoruntersuchung sowie der Antikörperbestimmung in Serum/Liquor. In der Serodiagnostik gelten monospezifische rekombinante Assays als Methode der Wahl und können mit konventionellen immunhistochemischen Nachweisverfahren kombiniert werden. Als Differenzialdiagnosen müssen infektiöse Enzephalitiden (v. a. HSV), andere autoimmune Ätiologien (z. B. limbische Enzephalitis mit Autoantikörpern gegen Hu, Ma2, CV2, Amphiphysin) sowie klinisch ähnliche Erkrankungen des zentralen und/oder peripheren Nervensystems ausgeschlossen werden. Eine diagnostische Abgrenzung zu atypischen Enzephalitiden sollte ebenfalls in Betracht gezogen werden. Es ist zu berücksichtigen, dass überlappende Symptome und Mischbilder unterschiedlicher Syndrome vorliegen können. Ein positiver serologischer Befund sollte eine umfassende Tumorsuche nach sich ziehen.
Die Diagnostik autoimmuner Enzephalitiden basiert im Allgemeinen auf der Kombination aus charakteristischem klinischem Bild, gegebenenfalls stützenden Befunden von Hirn-MRT, EEG und Liquoruntersuchung sowie der Antikörperbestimmung in Serum/Liquor. In der Serodiagnostik gelten monospezifische rekombinante Assays als Methode der Wahl und können mit konventionellen immunhistochemischen Nachweisverfahren kombiniert werden. Als Differenzialdiagnosen müssen infektiöse Enzephalitiden (v. a. HSV), andere autoimmune Ätiologien (z. B. limbische Enzephalitis mit Autoantikörpern gegen Hu, Ma2, CV2, Amphiphysin) sowie klinisch ähnliche Erkrankungen des zentralen und/oder peripheren Nervensystems ausgeschlossen werden. Eine diagnostische Abgrenzung zu atypischen Enzephalitiden sollte ebenfalls in Betracht gezogen werden. Es ist zu berücksichtigen, dass überlappende Symptome und Mischbilder unterschiedlicher Syndrome vorliegen können. Ein positiver serologischer Befund sollte eine umfassende Tumorsuche nach sich ziehen.
















 Die Diagnostik autoimmuner Enzephalitiden basiert im Allgemeinen auf der Kombination aus charakteristischem klinischem Bild, gegebenenfalls stützenden Befunden von Hirn-MRT, EEG und Liquoruntersuchung sowie der Antikörperbestimmung in Serum/Liquor. In der Serodiagnostik gelten monospezifische rekombinante Assays als Methode der Wahl und können mit konventionellen immunhistochemischen Nachweisverfahren kombiniert werden. Als Differenzialdiagnosen müssen infektiöse Enzephalitiden (v. a. HSV), andere autoimmune Ätiologien (z. B. limbische Enzephalitis mit Autoantikörpern gegen Hu, Ma2, CV2, Amphiphysin) sowie klinisch ähnliche Erkrankungen des zentralen und/oder peripheren Nervensystems ausgeschlossen werden. Eine diagnostische Abgrenzung zu atypischen Enzephalitiden sollte ebenfalls in Betracht gezogen werden. Es ist zu berücksichtigen, dass überlappende Symptome und Mischbilder unterschiedlicher Syndrome vorliegen können. Ein positiver serologischer Befund sollte eine umfassende Tumorsuche nach sich ziehen.
Die Diagnostik autoimmuner Enzephalitiden basiert im Allgemeinen auf der Kombination aus charakteristischem klinischem Bild, gegebenenfalls stützenden Befunden von Hirn-MRT, EEG und Liquoruntersuchung sowie der Antikörperbestimmung in Serum/Liquor. In der Serodiagnostik gelten monospezifische rekombinante Assays als Methode der Wahl und können mit konventionellen immunhistochemischen Nachweisverfahren kombiniert werden. Als Differenzialdiagnosen müssen infektiöse Enzephalitiden (v. a. HSV), andere autoimmune Ätiologien (z. B. limbische Enzephalitis mit Autoantikörpern gegen Hu, Ma2, CV2, Amphiphysin) sowie klinisch ähnliche Erkrankungen des zentralen und/oder peripheren Nervensystems ausgeschlossen werden. Eine diagnostische Abgrenzung zu atypischen Enzephalitiden sollte ebenfalls in Betracht gezogen werden. Es ist zu berücksichtigen, dass überlappende Symptome und Mischbilder unterschiedlicher Syndrome vorliegen können. Ein positiver serologischer Befund sollte eine umfassende Tumorsuche nach sich ziehen.